Many people often ask me, what is hydroponic gardening? Well, it’s a super cool way of growing plants without using any soil. Studies show it makes growing time faster and can significantly increase fruit and vegetable production.
This method has been around for centuries. However, modern technology is now making this way of cultivating plants more and more popular every day.
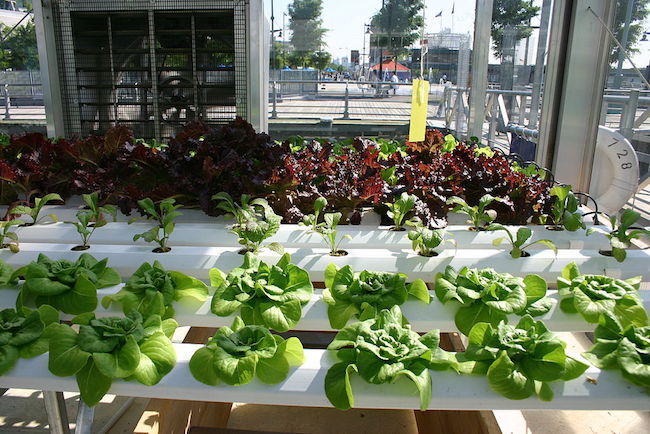

How Does Hydroponic Gardening Work?
Plants are fed with a specially made nutrient solution. The mineral rich fluid is delivered to the roots of plants by water or by air. These two ways are called “hydroponic” or “aeroponic” methods.

What? No Soil?
As an alternative for soil, growing plant roots are physically supported by a “growing medium”. The growing medium can hold water and nutrients, and is usually a porous substance.
Growing mediums can be made from many different materials including, clay, granite, treated glass or even plant material. Coco fibre from the outside of a coconut shell is a highly popular example.

You can grow flowers or food, using hydroponics, in limited space inside or outside of your home.
Simple System Example:

A Brief History
Because of all the fancy hydroponic gadgets kicking about today, many think that it’s a recent invention. However it’s actually been around for thousands of years.
Reputedly the Hanging Gardens of Babylon way back in 600 BC used this method of plant cultivation.
Hanging Gardens of Babylon (not an actual photo of course)

In the 10th and 11th century Aztecs were said to grow crops over lakes.
By placing their plants on floating rafts and letting the roots grow through into the water, they were using an early hydroponic system.
Famous accounts from the empire building Marco Polo state that he witnessed floating agriculture in China during the 13th century.
Real scientific analysis of the topic started in the 1600’s. Francis Bacon, a famous English scientist, artist, politician and philosopher researched the subject.
His book, which instigated huge interest in hydroponics, was published after his death in 1627.
The term “Hydroponics” was brought to light by Berkley scientist William Gericke in 1937. It comes for the Greek “hydro” meaning water and “ponics” meaning “work”.
Literally translated as – “Water Work” or “Working Water”
Hydroponics Are The Way Of The Future
Hydroponics are poised to be the growing method of the future. They can maximise growing space, crop quality and time to ripeness.
In our fast modern day world, new technology is dramatically improving this exciting approach to harvesting plants and food.
So much so that in Japan, USA and other countries experimental hydroponic farms are now being developed to grow vast amounts of fruits and vegetables indoors.

The latest and greatest of these is in Newark and is set to the the largest of it’s kind ever.
More and more news is appearing of the larger scale use of hydroponic technology for producing crops on a very large scale.
Benefits Of Hydroponic Gardening
- Hydroponic systems can be built in on many levels. Hence the sometimes used terms of “vertical gardening”, “vertical farming” or “vertical growing”.
- This means that small spaces in your home or garden can produce large amounts of crops because it is not limited to the actual floor space.
- As the method is suited to growing inside, food crops or flowers can be planted and grown all year round.
- Special lighting can also ensure optimal growth twenty four hours a day.
- Growing plants and food this way is very environmentally friendly and hence sustainable.
- No pesticides are required. Organic growing is a very real possibility.
- Anything from 80-95% less water is used by the plants. Way better than most large scale agriculture.
- It’s just as easy to do this type of horticulture outside as well as inside.
Main Hydroponic Setups
There’s six main types of hydroponic system.
-
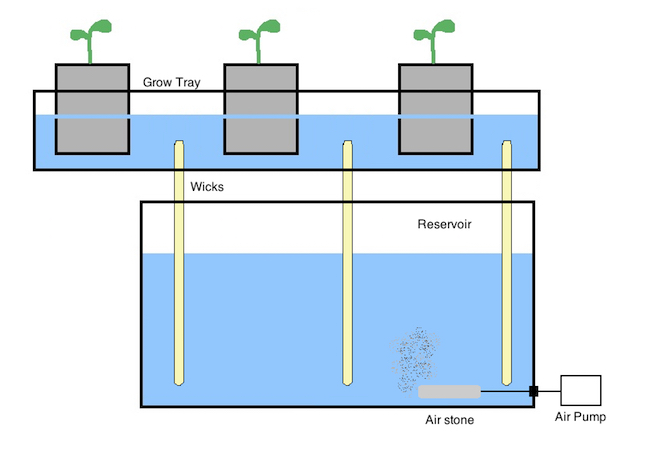
Wick Hydroponic Systems
The most simple of Hydroponic methods is the Wick system. This involves a two part contraption. The plants sit in a top layer with their roots inside the growing medium.
A bath of nutrient filled water sits under the plant layer. Nutrients are delivered to the growing medium and plant roots by a number of rope wicks. Hence the “Wick” system name.
No moving parts makes this a very low maintenance method. Because of this, wick systems are an excellent way to get started in soil free gardening. They are both simple to make and non time consuming to look after.
Herbs and leafy greens are ideally suited to this particular way of growing. Kitchen tops or large window ledges can easily cope with a home system of this type.
Break out the basil, and and get ready to grow some lush lettuce with this simple yet effective little system. The pump shown in this diagram is often not necessary and in fact is not normally used.
Positives: Really simple way to get yourself started.
Drawbacks: Limited to lettuces and herbs. Plants needing a lot of water e.g. tomatoes will not do well.
Good For: Lettuce and herbs like basil
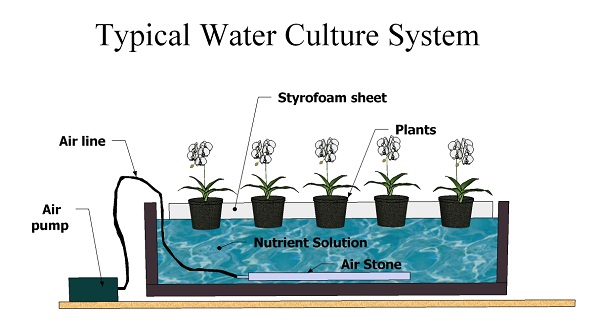
2. Water Culture
The Water Culture system includes just one tank. The tank is filled with water and the nutrient solution. The top of the tank has a covering. Small pots can be rested in holes of the covering. The roots of the plants then sit directly in the nutrient solution.
Air is fed to the plant roots via an air pump. The pump shoots air through a strip of air stones. The bubbles are nicely broken up by the air stones and spread them evenly throughout the mineral/water mixture. This helps the plants get their much needed supply of carbon dioxide.
Because of the pump which is a moving part, the water culture method is a member of the group called “active hydroponic systems”.
Due to its simple set up, it is also a hot favourite for educational purposes. Because it’s just a step up from the wicks system, it’s well suited for classroom demonstrations and new comers to active systems. (active systems have moving or electrical parts).
Positives: A great way to introduce newbies to “active” hydroponic systems. Active systems are ones with moving parts. In this case the air pump. Very simple to run.
Draw Backs: This method is really only suited to growing leafy greens such as lettuce. Not much else will flourish in this particular arrangement.
Good For: Lettuce and other leafy greens
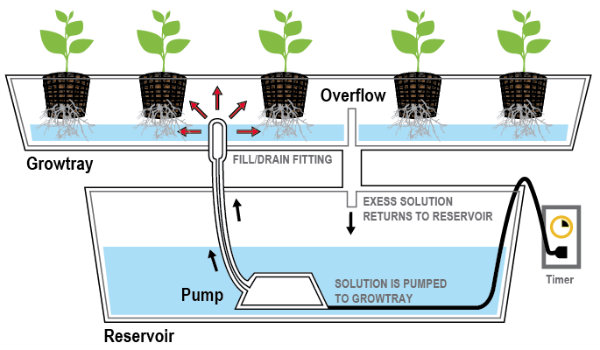
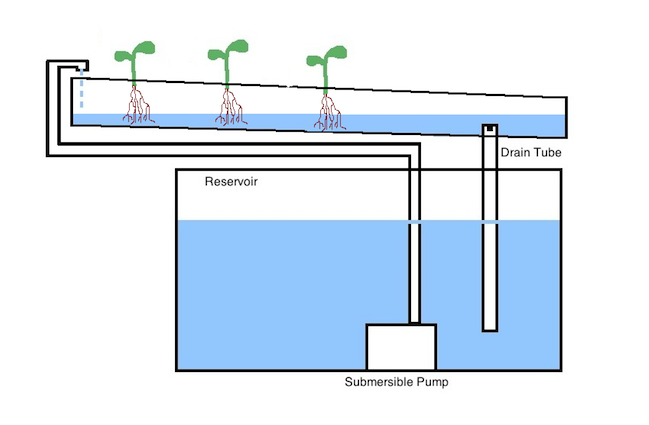
3. Ebb and Flow System (Flood And Drain)
Just like the ebb and flow of the ocean, this layout involves water going from high to low levels at regular intervals. Nutrient filled water is pumped to an upper tray where the plants are housed. This is then allowed to slowly drain off.
An intermittent timer sets off the water pump. This gives the water enough time to fill the upper tray, drain away, then refill the upper tray when suitable.
This cycle of pumping and draining (ebbing and flowing) is repeated about four times daily. This structure can be used for potted vegetables fruits or plants and is extremely adaptable,
It is also possible to fill the entire upper tray with growing medium. Plants can be then directly placed into that. Despite this, the preferred arrangement for most is to have individual pots with growing medium and plants inside of them.
These pots are then placed in the upper tray.
Positives: Very versatile, many different kinds of plants can be grown.
Drawbacks: Vulnerable to power cuts. Plants may dry out if the pump doesn’t work for a certain amount of time and the upper tray is not flooded. However this is unlikely.
Suitable For: A wide variety of vegetables and fruits can be grown. Anything that can grow in a pot basically.
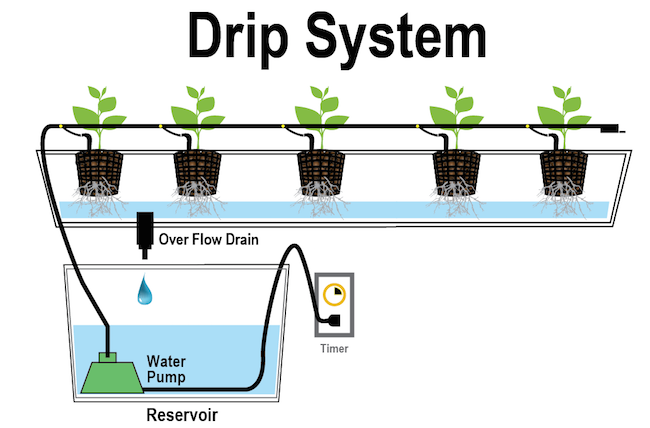
4. Drip System (recovery or non-recovery)
Drip drip drip. Yes you guessed it, this system works by dripping the nutrient solution onto the growing medium. The mineral mixture is aimed close to the plants and spreads throughout the growing tray.
This method is highly popular because the drip system can be applied at home or scaled up for commercial use. For this reason it is perhaps the most used Hydroponic system out there today.
Once again pumps are employed to deliver the mineral goodness from a reservoir and drip the solution in the correct place. In a recovery drip system the run off is “recovered” and recycled onto the plants.
Any run off goes back into the nutrient reservoir and is re-pumped back onto the growing tray. This makes for very efficient use of the nutrient solution.
In a non recovery drip system the mineral solution is not reused. It merely runs off and away. This may seem like a waste of good nutrients, however skilled timing and a precisely measured volume of the nutrients means very little will be wasted.
Most large scale use of this system uses the non recovery method.
Positives: Great for plants that require a lot of root space. Can grow anything.
Draw Backs: Large swings in PH due to increased concentration can happen in the recovery system. This may harm your plants. Checking PH at regular intervals is advised.
Suitable For: Everything.
5. N.F.T System
N.F.T stands for “Nutrient Film Technique”. Here the nutrient solution is pumped in a continuous flow over the plant roots.
It is released as a very shallow flowing stream creating a “film” of mineral dense water which gently flows over the roots.
No prizes for guessing where this system’s name comes from then!
In this particular hydroponic arrangement, there is no growing medium. The plants sit in a basket and the roots hang down into the flowing water.
Because of this the roots get an ample supply of both air and nutrients.
A slightly sloped tray allows the nutrient solution to run off. It is collected and usually recirculated over the roots again.
The combination of ample air and nutrients at the same time can make for fast growing and high yields.
Positives: Plants can get a perfect balance of nutrients and air. No growing medium reduces a great deal of hassle and expense.
Drawbacks: If the nutrient flow stops for any reason plants can be seriously harmed
Good For: Just about anything.
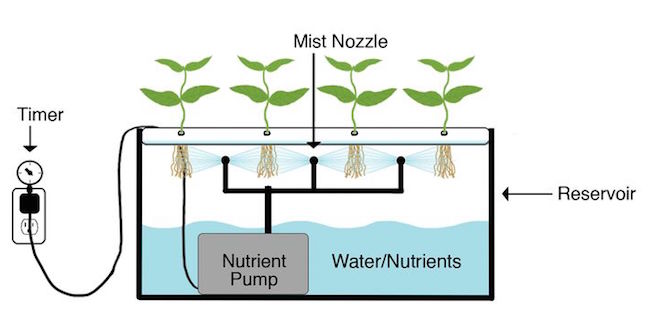
6. Aeroponic System
If you like gadgetry in your gardening this one’s for you. The aeroponic system periodically sprays plant roots with the mineral rich solution.
The plants sit on tray and the roots dangle into an enclosed compartment where the nutrient reservoir also sits.
Every few minutes the roots are sprayed with the nutrient solution. This creates a mist inside the enclosed chamber. The plants take this up to get their much needed nosh.
Like the NFT technique, in this system the roots get a good supply of both nutrients and air.
A timer controls the gaps between sprays. Spraying is needed every few minutes to stop the roots drying out.
Many ready to go hydroponic systems for your home use this set up.
Positives: Plants can get a perfect balance of nutrients and air.
Drawbacks: If there is a power cut or equipment failure roots will dry out very quickly.
Good For: Everything and anything you want.
Summary
Hydroponic gardening has many benefits including growing in small spaces, fast harvest time, higher yield and low environmental impact.
For these reasons it is fast becoming a popular agricultural method as well as a home hobby. Organic vegetables can be grown at home for all the family and it’s also very educational for kids.
Study Reference Nasa Study
What do you think? Do you think this is a good idea? Do you think it’s useful for us and the planet or is it a bad thing?
Please let us know in the comments below. Thanks.


Fascinating post thank you. I actually saw an example of hydroponic gardening this year while I was on holiday and it really sparked my interest. Would you say that using a Wick Hydroponic System would be best for a complete and utter newbie like myself? Pleased to find your site, thank you!
Hi there, yes I would say that the Wicks set up is a great way to get started. Once you have that going it’s easy to progress from there. Good luck!
What a well written article on hydroponic gardening!
I have been interested in setting up a hydroponics system myself for some years now. I do not have access to a garden as I live in a small flat. I would like to grow some herbs and maybe some small fruit/veg.
Would the wick system be suitable for this and would you say this is the best one for beginners? Also how much would it cost to set this up?
Thanks in advance.
Hannah.
Hi Hannah,
Glad you liked the article. Yes wicks is a great way to get started. You can only really grow lettuces and herbs, but it will still get you introduced to the world of hydroponic gardening.
You can make you own for as little as $30.
Interesting post. As a former Sous Chef, I always wondered what hydroponic meant whenever we purchased Boston/Bib lettuce. It’s crazy to think that hydroponic gardening has been around for thousands of years; and people like myself are just learning about it now!
I’m not 100% sure, but I believe Walt Disney World uses this method as well; I remember I took a tour of their gardens last year.
Thank you for sharing,
Diana
Thanks Diana I can imagine Disney world may well use hydroponics.
Hi Rob,
Wow! first time I saw different type of farming. I can’t believe, farming without soil. I agree to you of without soil it will minimize the growing of the pests that will destroy the growth and productivity of the plant. I am just bothered about the water nutrients mixture in this farming. Maybe for non edible plants I will not object. But the plants grown are to be eaten. Is this water nutrients mixture will not create health issues in the future?
By the way thanks for sharing this information. I really appreciate how well you presented your ideas. Good job!
marcy
Hi Marcy, Appreciate the compliments. The water mineral mixture is perfectly healthy. It is massively watered down before adding to the particular hydroponic system you are using. No detergents or bleaches etc. Just minerals and water. So it’s Ok.
This article has been very interesting for me. Now, I’m thinking of doing this but what kind of nutrients do I use, as I think I understood is that you don’t need the actual sunlight to grow plants. Its great way because I always tried to grow plants here but the soil is so salty, nothing comes out
Hi Fathima, there are many nutrient solutions that you can buy. I shall be adding some to this site very soon. The plants will need some light whether it is actual sun light or from a lamp of some kind. Thanks.
Hi!
I am a plant person too! And I really find it fascinating about the ancient aztecs, they were a truly intelligent people and way ahead of their time…. in some aspects of their society anyways.
Yes let’s not mention all the sacrificing!
Hi there Rob,i am happy to see there are other options out there that can be used in farming.It is good you have outlined the pros,space can be manipulated and this method can be used all year round.My worry is, what does the nutrient solution or growing medium consist of?I have a feeling these are chemicals used.How safe are these plants for human use,will it not expose people to chemical related or life style diseases?Just foot for thought!
Thanks for your comment Fmwaniki. Many people are quite rightly concerned about what goes into the nutrient solution for hydroponic gardening. There are no pesticides for starters. Please be aware that the word “chemicals” is misleading in many anti commercial farming websites. Water is a chemical for example and is not harmful. So not all chemicals are bad. The nutrient solution is merely a liquid fertiliser containing all the essential minerals for healthy plant growth. There are no added pesticides or harmful chemicals. Hope that puts you at ease. 🙂
Very interesting! I didn’t know a thing about hydroponic gardening before, now my curiosity is satisfied! It looks like a very natural way to feed vegetables, using no soil at all. By the way, the pictures of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and of the ‘Future Gardens’ are awesome! Can you tell me where did you get them?
Hi David, I’m glad you are satisfied! lol. If you do a google image search for either of those items you will find many similar images. Of course check first to see if they are under licence etc. Thanks for your comments.
Obviously I’d heard of hydroponics before, but never really understand the setup or how it worked. Thanks to your very detailed post on the subject I now feel I have a solid comprehension of the various systems. Definitely sounds like the way of the future for growing vegetables and things.
I love the bit of history you have included in this article, especially regarding the Hanging Gardens of Babylon.
Thanks Darren.
I’ve heard of hydroponics, and I always wondered how much does it cost to setup on of these to grow your own plants and food. Between the watering, the materials,etc, and the manpower needed.
It’d be awesome to grow your own food, to cut down on the grocery bill. 🙂
Thanks Tim, You can set up a simple system for as little as $50. But that might only grow things like herbs and lettuce. Keep an eye on the site for further developments. Thanks.
Nice article. Thanks for the advice. We like to buy organic, the only thing is that it can get expensive. Seems like it would be easier to do this at home since you don’t need soil. By showing the different methods to grow your garden, anyone can I apply the best method in their home.
Yes Andreas. You can even make your own system but buying the separate parts.This is cheaper way to do things. Thanks.
I have had some interest in learning about hydroponics for some time and this post gave me a good and easier to understand introduction to this topic than others. I like how you have covered so many different types of hydroponic systems which I didn’t even knew existed.
As I am the kind of guy that likes self-sustainability, I would be willing to consider hydroponics in the future only when I find a way to obtain nutrient solutions in a homemade manner as I would prefer to not have to depend on buying nutrient solutions repeatedly.
Thanks Bobby – I will look into home made nutrient solutions for you.
Interesting site!
I had never heard of hydroponic gardening until my son began studying about them in biology….
He recently brought home some lettuce that they had grown at school with this method.
It it is a very interesting concept and seems to have some real potential. I know he is enjoying the experience.
I will definitely be sending your site to my son!
Glad you like the site. I hope it gave you some good info. Lettuce is ideal for this kind of growing.
Hi Rob
I really, really loved reading this article.
Not only was it educational, but I really learned something from here.
My wife and I love to go the organic route when it comes to fruits and vegetables, we are picky and want the best for our bodies.
This idea of hydroponic gardening is something that got us both excited.
We are looking at the ‘Aerophonic System.’ What is the cost to start something like this up?
Thanks for a great read
Take Care
Roopesh
Hi Roopesh, glad you found the article interesting. The two recommended products I have on this site at the moment are the Tower Garden by Juice plus and the Grow up Hydrogarden. The juice plus tower is $500 but the Grow up Hydrogarden can be as little as $209.
What an amazing eye opener. I actually heard about hydroponic many years ago. But never start to look into this. I do not like to deal with soil, therefore this method is definitely suited for me. Do you know where I can buy all the tools required for hydroponic? I would love to buy a set to start my hydroponic farming. Please help
Hey Florence. I’m really glad the article has helped you. If you are looking to get started my main recommendation is the grow up hydrogarden which has all you need to get started for just $209.
Wow! Great article! I’d never heard of hydroponics ! It’s quite informative the way you presented it you know! I live in Iran but I will do my best to get the tools and work on my own garden.
Do you think they is shipping even to this side of the earth?
I’d appreciate any help
Thank you
Thanks Maryam. Yes i’m sure you can get going no matter where you are. You could even make your own system with pipes you can get from any garden centre.
Damn good article! I really enjoyed reading all of it. I have an interest on gardening some plants hydrophonically indoors. I think you can guess what i’m meaning 😉 But else of that it’s really great for modern indoor plantation. Also the history of hydrophonics was really interesting. Such easy principles and many useful applications can be applied to the technology.
Glad you enjoyed reading Tyler. Yes many different uses either for food or for flowers. The six basic models are just a starting point and can be assembled in sooooooooo many diferent ways.
Thank you for this very informative article! I did not know that the hanging gardens used hydroponics! That makes sense, though. How long have you been using hydroponics and what are the cheapest lights to get started with?
I’ve been using hydroponics for about six months now. I personally don’t use grow lights but this is another aspect that I will be looking into as soon as possible. I’m very glad you enjoyed the article Thomas.
Very inventive, yet the history behind it fascinates me. I mean, it was long practiced centuries ago and I guess it’s the lack of exposure.
Interesting tips and forms as they’re very distinctive. Not to mention that there’s no good or bad as there’s pros and cons.
You mentioned that it is considered to be educational. I agree. As a matter of fact, why not include as a syllabus for Science subject/project in school?
Hi Tar,
Thanks for the comments. I think one reason that Hydroponic gardening hasn’t been talked about a lot is that it’s been mainly for commercial use until quite recently. Also it has been associated with growing a certain illegal plant! However the uses for Hydroponics are wide and varied and can be scaled to whatever size or plants you wish. Yes it’s definitely a good educational tool and would be a good part of any early learning science class.
Wow!! Love your site! You really cover all the bases when it comes to hydroponics. It’s a facinating process and you make it understandable. I garden in an urban area and am always trying to find new ways to make use of my limited space. I have been considering hydroponics in a fence-like or trellis type structure.
Any ideas? I’ll be following you!
Depends. Do you want to make one yourself or buy a pre made kit??
I have been interested in this kind of gardening a while now. I grow organic veggies,fruit,flowers and herbs. Have you heard of aquaponics? What are your thought on that? I have a vinyl swimming pool and was thinking of trying to have fish and plants in the pool with a pump system of some kind? Could I just put plants in the pool? Thanks in advance.
Hi Tammy. Yes i’ve heard of aquaponics. Very clever idea creating a whole ecosystem with the fish and plants. I haven’t had any experience of it myself though.
I had no idea that hydroponic gardening was so ancient! That is so cool. I would love to grow some lettuce during the winter this way. Would it be easy to set something up inside a house for growing just some basic greens? Would you also need supplemental lighting?
How much would it cost to set up a basic system?
Hi Andrea, you can make a system pretty cheap if you want. Anything from $50 – $500 or you can even buy some pre-made systems which aren’t too expensive. Have a look in my product section at this nice model here. It’s just over $200. http://growgreenfood.com/grow-up-hydrogarden-review-2
I’ve been throwing around the idea of growing my own food for a while. Where can I find plans for building these systems? Does anyone make kits to get you started? Also where can you get the ingredients and instructions for the different solutions?
Hydroponic gardening looks like it would work great on a boat. My only concern is with some of the more complicated systems, how much power the pumps, timers, etc. will use.
I’m not sure about doing it on a boat. It’a probably better on a level surface or at least a stable one. As for building one yourself. I shall be adding a page about that very soon. Thanks Chris.
Hey, I’d never heard of hydroponic gardening before. This explains why I asked the question on your other post about how it’s possible to grow plants without using any soil. It’s really quite amazing that this method of growing plants goes back as far as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, and yet the standard way to grow plants seems to have been by using soil. Why do you think this is?
Glad you decided to read this article also Marcus. I think hydroponic gardening has not fully caught on yet because the technology for it to be done on an indistruial scale is only just emerging. Watch this space and see hydroponics become a far greater part of our food production over the next ten years.
Hey Robg, you seem to have an excellent knowledge on gardening. This Hydroponic gardening is completely alien to me and this is the very first time I am coming across this word. After reading your post, I got more interest in growing more plants and vegetables and leading a healthy and a organic life.
Hi Sundar, I’m very happy to have influenced you in that way. I hope you enjoy your Gardening experience!
This is great information! Thank you for providing so much detail. I have never really understood what hydroponic gardening was, and your post breaks it all down so that I understand and it makes sense! It is great that your provided pictures as well. I love to garden and I appreciate having other options to do so.
Thanks Ilysa, glad you were a little enlightened by the article. you should give it a try sometime.
Thanks Ilysa, glad you were a little enlightened by the article. you should give it a try sometime.
Now before I came to this website I had no idea what hydroponic gardening was. Basically growing plants without soil is interesting. I would love to see how food would taste fresh out of a hydroponic garden. To me it seems like a lot of work though. Just in my opinion. But overall very good material to be learned here.
Hi Good work. I totally understand how using a hydroponic system may seem like hard work. However, it ends up being easier than using normal gardening as you don’t need to do any weeding or worry about pests. generally the time to harvest is significantly faster also. Hope that helps. Rob.
Wow
I never really knew much about this hydroponic gardening before reading your article- even though it has been around for thousands of years it is completely new to me.
Amazing to consider able to garden without soil-sounds like something from the future not something possible today.
I am happy to experience your article today- it has interested me in this type of gardening very much.
Happy to have helped you out with a bit of knowledge. Please ask away if you want to know any more.
I love this article! Lots of people write about hydroponics but I have not seen the history discussed before. I did not know that the Aztecs used a floating system or that the Hanging Gardens of Babylon were reputed to have a hydroponic type system as well.
I also like the clear description of the pros and cons of each system. This makes it very clear what the options are!
I live in Alaska. We have great growing conditions in some parts of the state but not in others and certainly not in winter. Indoor hydroponic systems are starting up now.
Hey Rob
I love this post it was so interesting and informative. I have looked into Hydroponics a few times recently. I have not been able to start yet but it was great to read the various ways of doing it. I didn’t realize that there was different ways to do it. Thanks for this great post.
Kevin
It looks like the aeroponic system might work best for me. I really like that there is only one container that you would have to worry about. It means that the system would take up less space than the other options. Since I live in a smaller apartment, I don’t have space for a big huge system.
Yes a one container aeroponic set up could be good for you. If saving space is your main concern a water culture system would do just as well.
Great article! I really enjoyed reading it and found it very interesting. With better results and more spaced saved, clearly these systems will take over.
My garden is just filled with patio so there’s no way I could grow my own crops and plants the conveintional way. Making these methods much more suitable for me, I’ll make sure to keep my eye out for them and maybe I’ll even try it in the coming years.
Thanks Lyle, appreciated. Hydroponics definitely helps with lack of space. However if you don’t want to get too technical, clever use of window boxes or other containers will still help on a patio.
Wow, hydroponic gardening sure sounds promising! This is all new to me, so there’s a lot of good information on here. I’ve been wanting to try to grow herbs and lettuce in my house during the winter months. I imagine the wick hydroponic setup would be the easiest if I wanted to setup an indoor garden? Do you know where I would get the rope wicks from? Or is this something I would be able to make?
Hi Eisa, Thanks for the comment. Really any kind of rope or string will do. Bigger plants need bigger rope however. Thanks.